Metformin Safety: What You Need to Know About Side Effects, Interactions, and Long-Term Use
When it comes to managing type 2 diabetes, metformin, a first-line oral medication used to lower blood sugar by reducing liver glucose production and improving insulin sensitivity. Also known as Glucophage, it’s been the go-to drug for decades because it works, doesn’t cause weight gain, and rarely triggers low blood sugar. But safety isn’t just about whether it lowers glucose—it’s about what else it does to your body over time.
One of the biggest fears around metformin, a biguanide-class diabetes drug is lactic acidosis, a rare but serious buildup of lactic acid in the blood. It’s not common—less than 1 in 10,000 users—but it’s more likely if you have kidney problems, heart failure, or drink alcohol heavily. That’s why doctors check your kidney function before and during treatment. If your eGFR drops below 30, metformin is usually stopped. But if it’s between 30 and 45, many providers still use it cautiously, especially if you’re otherwise healthy.
Another real concern is metformin interactions, how other drugs can change how metformin works or increases side effects. For example, certain contrast dyes used in CT scans can temporarily harm kidney function, which raises lactic acidosis risk. That’s why you’re told to pause metformin before and after the scan. Some antibiotics, diuretics, and even over-the-counter NSAIDs can affect kidney clearance too. And if you’re taking other diabetes meds like sulfonylureas or insulin, you might see better blood sugar control—but also a higher chance of low glucose, even though metformin itself rarely causes it.
Long-term use brings other questions. Many people report stomach upset—diarrhea, nausea, gas—especially when starting. But that often fades. Taking it with food helps. There’s also evidence that metformin lowers vitamin B12 levels over time, which can lead to nerve issues or anemia if not monitored. Simple blood tests can catch this early. And while some studies suggest metformin might help with weight loss or even slow aging, those are still being researched. Don’t take it just because you heard it’s a "miracle drug." It’s not.
What you’ll find below are real-world stories and science-backed advice on how to use metformin safely. From how to spot early signs of trouble, to which drugs to avoid, to what your doctor should be checking every year—you’ll see exactly what works and what doesn’t. These aren’t theoretical guides. They’re written by people who’ve been there: pharmacists who caught errors, patients who adjusted their routines, and clinicians who’ve seen the consequences of ignoring the small details.
Metformin Side Effects: How to Manage Gastrointestinal Issues and Understand Lactic Acidosis Risk
Metformin is the first-line treatment for type 2 diabetes, but gastrointestinal side effects are common and lactic acidosis is a rare but serious risk. Learn how to manage stomach issues, recognize warning signs, and stay safe while taking this essential medication.
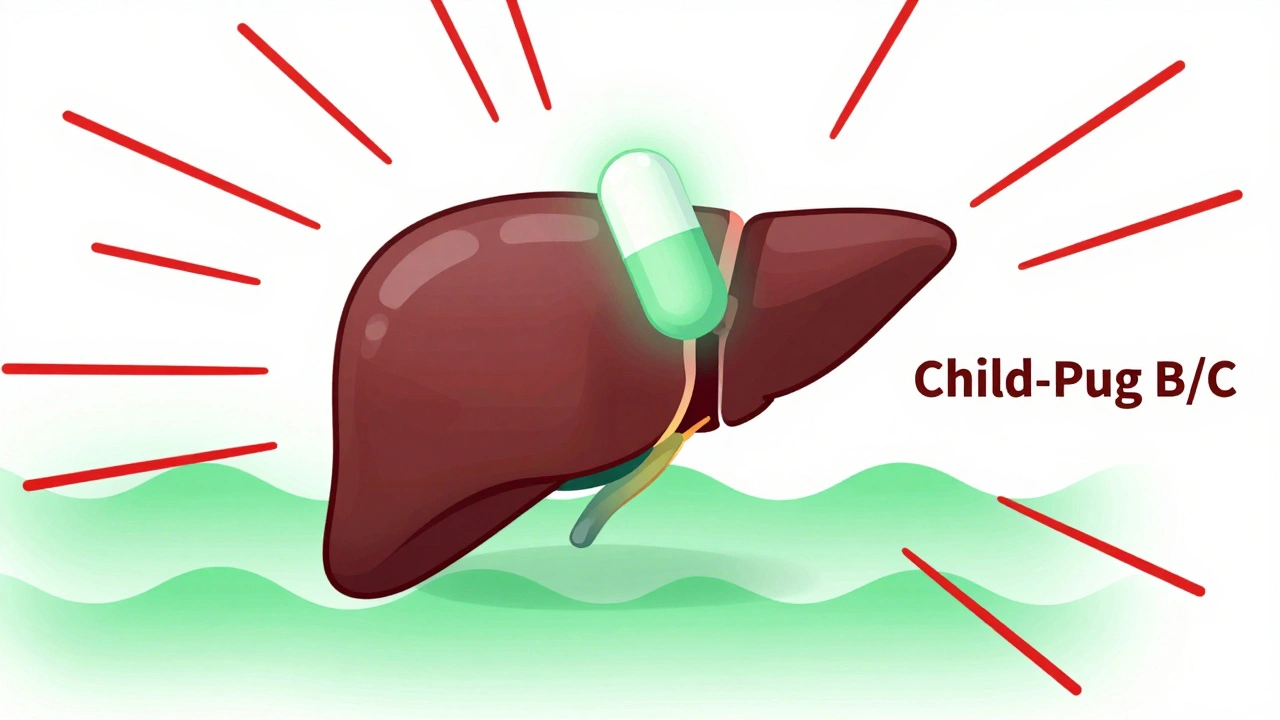
Metformin and Liver Disease: How to Prevent Lactic Acidosis
Metformin is safe for many people with mild liver disease and may even help protect the liver. Learn when it's safe to use, how to prevent lactic acidosis, and what alternatives exist.