Selegiline: What It Is, How It Works, and What You Need to Know
When you hear selegiline, a selective monoamine oxidase-B inhibitor used to treat Parkinson’s disease and sometimes depression. Also known as L-deprenyl, it works by helping your brain hold onto more dopamine—the chemical that controls movement and mood. Unlike older drugs that flood your system with chemicals, selegiline quietly protects what’s already there. It doesn’t add dopamine; it stops your body from breaking it down too fast. That’s why it’s still in use decades after it was first approved.
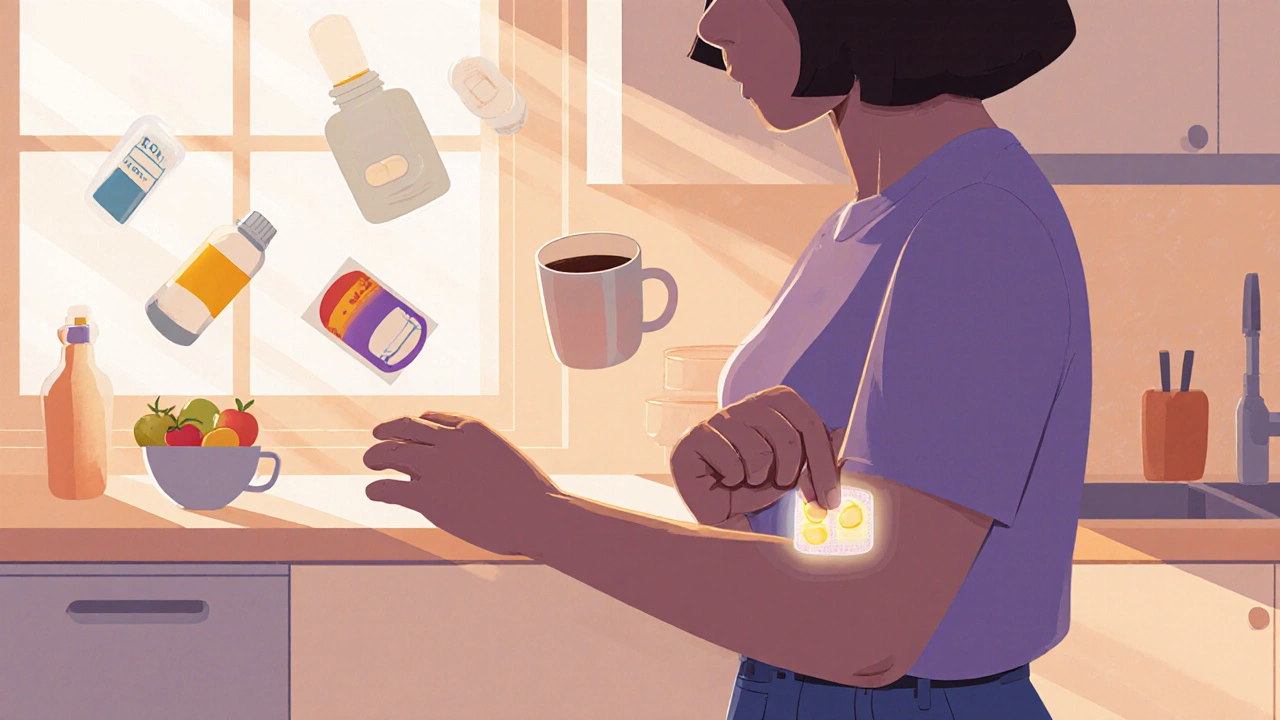
Selegiline is often paired with levodopa, the main treatment for Parkinson’s. Together, they help reduce tremors, stiffness, and slow movements. But it’s not just for Parkinson’s. Some doctors prescribe it for depression that hasn’t responded to other meds, especially when fatigue and low energy are the main problems. It’s not a quick fix, but for some people, it’s the only thing that makes a real difference. The patch form, which goes on your skin, avoids stomach side effects and gives steadier levels in the blood—something many patients prefer over pills.
It’s not without risks. Taking selegiline with certain foods, other antidepressants, or even some over-the-counter cold meds can trigger dangerous spikes in blood pressure. That’s why your doctor will ask about everything you’re taking. It also doesn’t work the same for everyone. Some feel more alert and focused; others get insomnia or dizziness. If you’re on it, you’ll need regular check-ins to make sure the dose is right and nothing’s building up in your system.
Related to selegiline are other MAO-B inhibitors, drugs that block the same enzyme to preserve dopamine. Rasagiline and safinamide are newer options that work similarly but may have fewer dietary restrictions. If you’ve tried selegiline and didn’t like the side effects, these might be worth discussing with your doctor.
People with Parkinson’s aren’t the only ones using it. There’s growing interest in how selegiline affects brain aging and neuroprotection. Some studies suggest it might slow the loss of dopamine neurons over time, though that’s still being researched. It’s not a miracle drug, but for those who’ve tried everything else, it can be a lifeline.
What you’ll find in the posts below are real-world stories and facts about selegiline and the medications it’s often used with—like how it interacts with antidepressants, what to do if you miss a dose, and why some people switch to the patch. You’ll also see how it fits into broader treatment plans for movement disorders and mood conditions. No fluff. Just what works, what doesn’t, and what you need to watch out for.
Compare Emsam (Selegiline) with Alternatives for Depression Treatment
Emsam (selegiline) is a patch-based antidepressant for treatment-resistant depression. Learn how it compares to SSRIs, other MAOIs, bupropion, and esketamine - and which option might be right for you.